Epilepsy Key facts
➥A neurological disorder affecting individuals of all ages, epilepsy is a long-term, noncommunicable condition.
➥Epilepsy affects about 50 million people around the world, making it one of the most common brain diseases in the world.
➥Epilepsy affects almost 80% of people who live in low and middle income countries.
➥With the right diagnosis and treatment, up to 70% of persons with epilepsy could live seizure-free.
➥People with epilepsy have up to three times higher risk of early death than the general population.
➥People with epilepsy and their families face abuse and shame in many parts of the world.
What is Epilepsy?
➥ Epilepsy is a brain disorder that makes people more likely to have spontaneous seizures over and over again. It's a very common problem with the nervous system that can happen to people of any age, race, or class. About 3 million Americans have epilepsy, and every year about 200,000 new cases are found, according to the CDC.
➥ A seizure can be caused by anything that stops the brain's nerve cells from connecting normally. This includes having a high fever, low blood sugar, going through withdrawal from drugs or alcohol, or getting a brain injury. This makes it possible for anyone to have one or more seizures. But someone is thought to have epilepsy if they have two or more seizures that don't have a cause. Epilepsy can be caused by a number of things, such as an excess of neurotransmitters (chemicals that send messages between nerve cells), tumors, strokes, and brain damage from illness or injury, or a mix of these. Most of the time, there may not be a clear reason why someone has seizures.
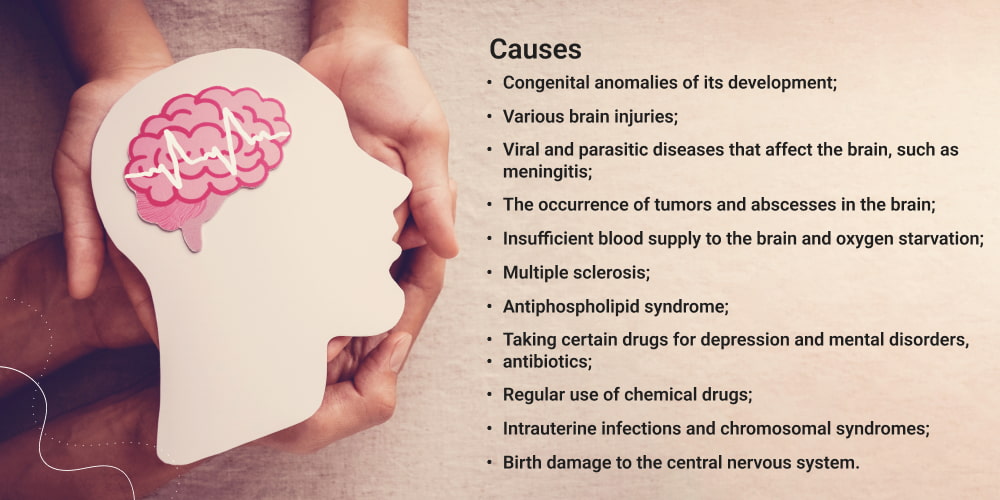
What Causes Epilepsy?
➥ The exact cause of epilepsy is often unknown. However, potential triggers include:
❃Genetic Factors: Some types of epilepsy run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
❃Brain Injuries: Trauma, stroke, or infections like meningitis can lead to epilepsy.
❃Developmental Disorders: Conditions like autism or neurofibromatosis are linked with epilepsy.
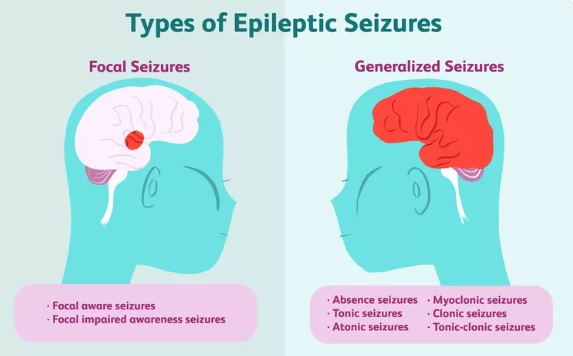 Types of Epilepsy Seizures
Types of Epilepsy Seizures
Epilepsy seizures are broadly categorized into two types: focal (or partial) seizures and generalized seizures. Based on the signs and symptoms a person has, these types of seizures are further broken down into subtypes. Some people with epilepsy have more than one type of seizure, but most only have one or two.
➥ The three primary seizure types are:
- focal seizures
- generalized seizures
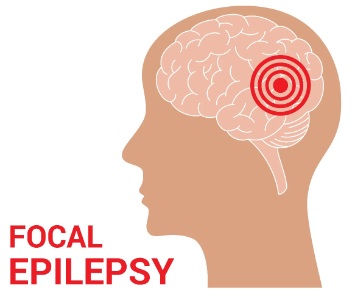
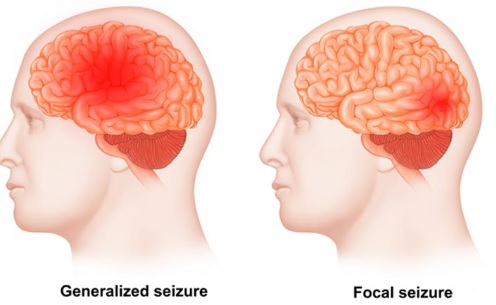
1.Focal-Onset Seizures
Focal seizures are the most common type of seizures. They start in one area of the brain and manifest in different ways depending on which area they impact.
Focal seizures can happen to both kids and adults, according to doctors. About six out of ten people who have epilepsy have isolated seizures.
➥ What focal seizures feel like depends on what part of the brain is hurt. Some of them are:
- A feeling of déjà vu (like the moment has happened before).
Changes in smell or taste that happen quickly.
Hallucinations are when you hear or see things that aren't there.
- An intense feeling of fear, joy, anger, or sadness.
- Swelling or rigidity in a single area (such an arm or face) or side of the body.
- Lip-smacking.
- Rapid heart rate.
- One side or part of the body feeling numb or tingly.
➥ In focal seizures, there are three different types:
❃ Focal aware seizures:
The person is fully aware of their symptoms and is having this type of seizure. One treatment for focal seizures is Gabapentin 100mg, also known as Neurontin.
❃ Focal impaired awareness seizures
There is more damage to the brain in these seizures than in focal aware seizures. When someone is having this kind of seizure, they might be confused and not know what's going on around them.
❃ Focal-to-bilateral tonic-clonic seizures
Some people who have epilepsy go from having a focal seizure to having action on both sides of their brain during the focal seizure. It's important to know where in the brain focal-to-bilateral tonic-clonic seizures begin because they can look like they start in the whole brain. There may be different ways to treat focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizures than generalized start seizures. Focal seizures are also called partial seizures, and doctors treat them with Gabapentin 800mg and other drugs.
If someone is aware of their first symptoms (the ones listed above), they may be able to get to a safe place before they lose consciousness or start having a bilateral tonic-clonic seizure. This can help them avoid falling and getting hurt.
2.Generalized onset seizures
A generalized onset seizure can happen on either side of the brain. These happen without warning, which means there will be no an aura before they happen.
When seizures happen in both sides of the brain, this is called a generalized seizure. Most of the time, these seizures happen because the electrical activity in the brain is out of balance between pathways that slow down or speed up activity.
Current research is looking into how genetics may play a role in the development of generalized seizures. Yet, only a small percentage of people who have these kinds of seizures have family members who also have the condition.
One of the most important signs that someone is about to have a seizure is if they feel a "aura" before the seizure starts. Senses and emotions that aren't normal come after the "aura."
➥ Then seizure signs show up, such as:
- Fast blinking
- Loss of consciousness
- Uncontrolled muscle movements
- Body convulsions or epileptic spasms
- Repetitive movements
- Blue lips
➥ The following are some types of generalized seizures:
❃ Absence Seizures:
Seizures of Absence which used to be called "petit mal" seizures, happen more often in kids. People sometimes think that this kind of seizure is just thinking because it can last for only a few seconds. The person usually doesn't react, but if they are having a "atypical" absence seizure, they might be able to speak a little.
❃ Atonic Seizures:
Antonic Seizures These go also under the names "drop attacks" or "drop seizures." The person's usual resting muscular tension, sometimes known as "tone," goes limp. If they're sitting, they might suddenly slump over. They might fall to the ground like a rag doll if they are standing.
❃ Myoclonic Seizures:
Seizures with myoclonus People who have these seizures feel like they've been shocked by electricity because their muscles tense up quickly. A myoclonic seizure is like the rapid jerks people often feel as they fall asleep, but these "sleep myoclonic" jerks aren't dangerous, but myoclonic seizures are. Infantile spasms are a type of myoclonic seizures that usually start in kids between 3 and 12 months old and can last for years. They usually start with a quick jerk and then get stiff. For a child, this very bad type of epilepsy can have long-lasting affects.
❃ Tonic Seizures:
Stroke of Tonic During this type of seizure, the person loses awareness and their muscles stiffen all of a sudden. They might fall to the ground too, but it will be more like a tree trunk than a rag doll. Gabapentin 300mg is a medication often prescribed for the management of seizures, including those associated with generalized epilepsy.
❃ Clonic Seizures:
Clonic Seizures Muscles jerk and twitch during this type of seizure. Elbow, leg, and neck muscles flex and relax quickly one after the other. The shaking motion gets less severe as the seizure goes away and then stops completely.
❃ Tonic-Clonic Seizures:
Seizures with Tonic-Clonic People usually think of epilepsy when they see these kinds of seizures, which used to be called "grand mal" seizures. The person stiffens up, like during a tonic seizure, and then their muscles start to jerk, which is called "clonus."
Do what you can to keep the person safe and write down the time if you see someone having what looks like any kind of seizure. Tonic-clonic seizures that last more than 5 minutes are a medical emergency, and you should call 911 if you see one.
People who are having a tonic-clonic seizure might lose control of their stomach or bladder. They will also be tired and sore after the seizure, which is called the "postictal" period.
Final Word:
People with epilepsy have seizures that happen over and over again. These seizures are caused by electrical activity in the brain that can't be managed.
These can lead to a lot of different symptoms, like losing awareness, jerking limbs, not being able to control your bladder, feeling sleepy, and having strange tastes and smells. Buy Now Gabapentin is an effective medication for managing partial seizures and can be used as part of a combination therapy for generalized seizures when other treatments are inadequate.
When someone has generalized epilepsy, their whole brain is affected, but when someone has localized epilepsy, only a part of the brain is affected.
Then, epilepsy can be broken down further based on other signs, such as whether the person is aware of their surroundings during the episode, and what muscles and movements are involved.
It's called "unknown onset" when it's not clear what kind of seizure someone is having until more tests can confirm the diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can epilepsy be cured?
No, epilepsy cannot be cured, but it can be managed effectively with medication and lifestyle adjustments.
Q: Are all seizures the same?
No, there are various types of seizures, each with different characteristics and symptoms.
Q: Can stress trigger a seizure?
Yes, stress is a common trigger for seizures in many individuals with epilepsy.
Q: Is epilepsy hereditary?
Some forms of epilepsy have a genetic component and can run in families.
Q: Can children outgrow epilepsy?
Some children may outgrow epilepsy, especially if they have certain types of childhood epilepsy that tend to resolve with age.


Fantastic site A lot of helpful info here Im sending it to some buddies ans additionally sharing in delicious And naturally thanks on your sweat
I do believe all the ideas youve presented for your post They are really convincing and will certainly work Nonetheless the posts are too short for novices May just you please lengthen them a little from subsequent time Thanks for the post
Wow wonderful blog layout How long have you been blogging for you make blogging look easy The overall look of your site is great as well as the content